Practice finding security vulnerabilities within ZAP or the Broken Web App by running SCA, SAST, DAST, IAST using open-source SonarQube, Sonatype, Synopsys and other tools
Overview
- Why this?
- Sample broken apps
- DVIA iOS App Mobile Testing
- Software Testing Guidelines
- Security Testing Tools
- Install proxy server
- Instantiate within Google Cloud
- Browser Proxy Setup
- Install Jenkins plugin
- ZAP UI OWASP
- ZAP scripts
- Vendors
- Other DAST vendors
- SARIF
- Resources
- More on Security
- More on DevOps
Why this?
Threat hunting is a proactive approach to detecting and mitigating threats. It is a continuous process of searching for, identifying, and mitigating potential threats in your environment.
OWASP Web Top 10
OWASP is a non-profit organization with a mission to provide practical vendor-neutral information about application security.
OWASP (Open Web Application Security Project) Top 10 - 2017 PDF: is the result of an on-going active non-profit team.
The OWASP Top 10 Web Application Security Risks was updated in 2021.
YouTube videos from F5 DevCentral 2017 by John Wagnon (and Description from OWASP):
Also: Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF)
Coding Errors
Top 25 Common Weakness Enumeration (CWE): category system for software vulnerabilities and weaknesses.
There is also SAN’s Top 25 Software Errors that include
- Insecure Interaction Between Components,
- Risky Resource Management, and
- Porous Defenses
OWASP API Security Top 10
API security Top 10 had 2019 and 2023 versions. Courses are from APISec.ai.
-
API1:2023 Broken Object Level Authorization (BOLA)
CLASS: This is the most common AND damaging API vulnerability, resulting in data loss, disclosure, data manipulation. APIs can expose endpoints that handle object identifiers, creating a wide attack surface Level Access Control issue. Object level authorization checks should be in every function that accesses a data source using an input from the user. An example is authenticated User A retrieves user B’s private data. Prevention:
- Define data access policies and implement them in the business logic of the API.
- Enforce data access controls on the server-side, not just the client-side.
- Implement horizontal access control checks to ensure one user cannot access another user’s data.
-
API2:2023 Broken User Authentication
CLASS: Authentication mechanisms are often implemented incorrectly, allowing attackers to compromise authentication tokens or to exploit implementation flaws to assume other user’s identities temporarily or permanently. Compromising system’s ability to identify the client/user, compromises API security overall.
-
API3:2023 Broken Object Property Level Authorization (BOPLA)
CLASS: Looking forward to generic implementations, developers tend to expose all object properties without considering their individual sensitivity, relying on clients to perform the data filtering before displaying it to the user.
-
API4:2023 Broken Object Property Level Authorization
CLASS: Quite often, APIs do not impose any restrictions on the size or number of resources that can be requested by the client/user. Not only can this impact the API server performance, leading to Denial of Service (DoS), but also leaves the door open to authentication flaws such as brute force.
-
API5:2023 Unrestricted Resource Consumption (Lack of Resources & Rate Limiting)
CLASS: Previously Broken Function Level Authorization. Complex access control policies with different hierarchies, groups, and roles, and an unclear separation between administrative and regular functions, tend to lead to authorization flaws. By exploiting these issues, attackers gain access to other users’ resources and/or administrative functions.
-
API6:2023 Unrestricted Access to Sensitive Business Flows
CLASS: (Mass Assignment) Binding client provided data (e.g., JSON) to data models, without proper properties filtering based on a whitelist, usually lead to Mass Assignment. Either guessing objects properties, exploring other API endpoints, reading the documentation, or providing additional object properties in request payloads, allows attackers to modify object properties they are not supposed to.
-
API8:2019 Security Misconfiguration
CLASS: Security misconfiguration is commonly a result of unsecure default configurations, incomplete or ad-hoc configurations, open cloud storage, misconfigured HTTP headers, unnecessary HTTP methods, permissive Cross-Origin resource sharing (CORS), and verbose error messages containing sensitive information.
Injection flaws, such as SQL, NoSQL, Command Injection, etc., occur when untrusted data is sent to an interpreter as part of a command or query. The attacker’s malicious data can trick the interpreter into executing unintended commands or accessing data without proper authorization.
-
API9:2023 Improper Inventory Management
CLASS: APIs tend to expose more endpoints than traditional web applications, making proper and updated documentation highly important. Proper hosts and deployed API versions inventory also play an important role to mitigate issues such as deprecated API versions and exposed debug endpoints.
CLASS: Insufficient logging and monitoring, coupled with missing or ineffective integration with incident response, allows attackers to further attack systems, maintain persistence, pivot to more systems to tamper with, extract, or destroy data. Most breach studies demonstrate the time to detect a breach is over 200 days, typically detected by external parties rather than internal processes or monitoring.
Kubernetes Top 10
https://owasp.org/www-project-kubernetes-top-ten
- K01: Insecure Workload Configurations
- K02: Supply Chain Vulnerabilities
- K03: Overly Permissive RBAC Configurations
- K04: Lack of Centralized Policy Enforcement
- K05: Inadequate Logging and Monitoring
- K06: Broken Authentication Mechanisms
- K07: Missing Network Segmentation Controls
- K08: Secrets Management Failures
- K09: Misconfigured Cluster Components
- K10: Outdated and Vulnerable Kubernetes Components
https://www.redhat.com/en/resources/state-kubernetes-security-report-2023
https://www.cisecurity.org/benchmark/kubernetes
OWASP Top 10 for LLMs (AI/ML)
https://snyk.io/blog/addressing-risks-in-the-owasp-top-10-for-llms/
APISec Test results
- Fail “positive” tests when API functionality is found to not operate as expected according to the API specification.
- Fail “negative” tests when the API is found vulnerable to attacks imposed by testing tools.
Only 4% of API testing focuses on security, according to Gartner.
One vendor’s API test results are organized into four categories:
A. Vulnerable
- Injection (Log4J):
- Fuzzing (random data):
- Reflected Injection:
B. Valuable
- Personal Data
C. Configuration
- SSL Certificate
- SSL Required
- Server Properties Leak
- HTTP Options
- CORS Configuration
- Incremental IDs
D. Authentication
- Broken Authentication
Testing is based on lists of vulnerabilities identified by OWASP, SANS, and other organizations.
PCI DSS v4 API Requirements
PCI DSS v4.0 is a 360-page PDF published June 2022, with a deadline of 31 March 2024. It addresses API risks for the first time.
The previous verion, PCI DSS v3.2.1 is a 139-page PDF.
The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) is a proprietary information security standard for organizations that handle branded credit cards from the major card schemes including Visa, MasterCard, American Express, Discover, and JCB.
https://www.pcisecuritystandards.org/ PCI Security Standards Council
https://blog.pcisecuritystandards.org/pci-dss-v4-0-resource-hub PCI DSS 4.0 Resource Hub
https://www.pcisecuritystandards.org/document_library/ PCI Document Library
https://listings.pcisecuritystandards.org/documents/PCI_DSS-QRG-v3_2_1.pdf PCI DSS Quick Reference Guide (PDF)
v1.0 was published in 2004.
Despite v1.1 in 2006, TJMax was hacked in 2007 (45M). Heartland Payment Systems was hacked in 2008 (130M).
Cardholder data (CHD) is the full Primary Account Number (PAN) or the full PAN along with any of the following elements:
- Cardholder name
- Expiration date
- Service code
Sensitive authentication data (SAD) is the full magnetic stripe data, CAV2, CVC2, CVV2, CID, PINs, and PIN blocks.
PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) Standards:
- PTS (PIN Transaction Security)
- PA-DSS (Payment Application Data Security Standard)
- P2PE (Point-to-Point Encryption)
- PCI PIN (PCI PIN Security Requirements)
- PCI SPoC (PCI Software PIN on COTS)
- PCI CPoC (PCI Contactless Payments on COTS)
- PCI DSS SAQ (PCI DSS Self-Assessment Questionnaire)
- PCI DSS ROC (PCI DSS Report on Compliance)
- PCI DSS AOC (PCI DSS Attestation of Compliance)
- PCI DSS QSA (PCI DSS Qualified Security Assessor)
- PCI DSS ASV (PCI DSS Approved Scanning Vendor)
- PCI DSS ISA (PCI DSS Internal Security Assessor)
- PCI DSS QIR (PCI DSS Qualified Integrator and Reseller)
Other Standards
-
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
-
Motor Industry Software Reliability Association (MISRA) C/C++ coding standards
-
CERT C/C++, CERT Java, CERT Python?
-
(US) DISA STIG,
-
ISO 26262
-
ISO/IEC TS 17961
-
AUTOSAR®
Sample broken apps
Several apps have been created to exhibit vulnerability issues, as examples for testing tools.
Such apps should run only inside a guest machine within VirtualBox or VMware set to NAT networking mode.
CAUTION: Do not upload it to your hosting provider’s public html folder or any Internet-facing servers, as they will be compromised. If you run security vulnerability tests against a server you don’t control, you are hacking that site. So get both an NDA and contract of scope of work before starting.
AWS Goat
VIDEO: https://github.com/ine-labs/AWSGoat provides two web apps containing OWASP Top 10 web application security risks (2021):
- A Python3 AWS Lambda React blog using DynamoDB with misconfigured AWS resources.
- An HR Payroll PHP app running on Terraform-built EC2 with misconfigured S3 buckets.
Blogs: - https://alparslanakyildiz.medium.com/aws-cloud-pentesting-notes-9dc9e75cbed8
- https://ine.com/blog/awsgoat-a-damn-vulnerable-aws-infrastructure
- https://www.helpnetsecurity.com/2022/08/10/awsgoat-vulnerable-aws-infrastructure-video/
Metasploitable3
Metasploitable3 from Rapid7 is a victim VM created with intentional vulnerabilities for abuse by Metasploit and other ethical hacking tools running in Kali OS. See Metasploit Unleashed at Offsec.com.
Instructions below provide manual steps to use Dean Bushmiller’s VIDEO describing the GitHub he used to setup Kali Linux VMs as AMIs:
TODO: Create script to do the below.
-
Sign in the AWS Console GUI to the region Dean used to create his AMIs:
https://us-east-1.console.aws.amazon.com/
-
Click the CloudShell icon, for a URL such as:
https://us-east-1.console.aws.amazon.com/cloudshell/home?region=us-east-1
-
Highlight and copy the single command below
aws ec2 copy-image --name kali-linux --source-image-id ami-0e0c5931cfadd2102 --source-region us-east-1 && aws ec2 copy-image --name metasploitable3-linux --source-image-id ami-0b186198cc048aa9d --source-region us-east-1 && aws ec2 copy-image --name metasploitable3-windows --source-image-id ami-0e3153815a2b50c67 --source-region us-east-1
PROTIP: The AMI id’s above are for us-east-1 only. Changing those regions would require other AMIs to be created.
-
Paste in the CloudShell and press Return to execute.
If you get a “500 - Internal Server Error”, refresh the page.
The expected response are new ImageIds:
{ "ImageId": "ami-0e0c5931cfadd1111" } { "ImageId": "ami-0b186198cc0482222" } { "ImageId": "ami-0e3153815a2b53333" }NOTE: AWS charges are not incurred until these instances are launched.
-
Duplicate another AWS browser tab and search for the “EC2” service for your region, for a URL such as:
https://us-east-1.console.aws.amazon.com/ec2/home?region=us-east-1#Home:
-
Click “Snapshots” in the left or middle menu to see a list of the AMIs created above.
For use to SSH into the instance
-
Click “Key Pairs” in the left menu
https://us-east-1.console.aws.amazon.com/ec2/home?region=us-east-1#KeyPairs:
- Click the orange “Create Key Pair”
-
Type a Name such as “kali-linux-231231” and click “Create key pair”.
Leave defaults RSA for Key Pair type and .pem for use with OpenSSH.
-
Navigate to the folder where the .pem file is downloaded.
My IP Address
To find the public IP address of your laptop:
-
In an internet browser such as Chrome, click this URL:
You will later highlight and copy the IPv4 address displayed.
-
Open another browser tab so you can return to the above page.
Cloud Formation
-
Search for the “Cloud Formation” service for your region, for a URL such as:
https://us-east-1.console.aws.amazon.com/cloudformation/home
-
Click the drop-down “Create Stack” and select “With New Resources (standard)” for the page with default “Template is ready” and “Amazon S3 URL”
-
Copy the URL below to paste into the “Amazon S3 URL” field:
https://ceh-v11-20220609.s3.amazonaws.com/20220715-LAB-Pentest/pentestlab.yml
That file was create by Dean and has contents beginning with:
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: 2010-09-09 Description: Penetration Testing Lab Environment V20221102
- Click “Next” for the “Specify stack details” page.
-
For Stack name, type your unique name and today’s date, such as
johndoepentestlab231231a
No spaces are allowed in Stack names. because they are used in URLs.
-
Switch back to the tab for the CloudShell to highlight and copy each of the ami-xxxxxx values.
- In the AttackerAMIId field, paste from above the first AMI id, for Kali Linux.
- In the LinuxVictimAMIId field, paste from above the second AMI id.
- In the WindowsVictimAMIId field, paste from above the third AMI id. (Windows 2008 R2)
- In the PublicAddress field, find your public IP address by searching for “what is my ip” in a browser at https://whatismyipaddress.com/
- Click the SSHKeyPair field and select the key pair you created above.
- Click “Next” for the “Configure stack options” page.
- Click “Next” for the Review page.
- Click “Estimate cost” to see the cost of running the stack.
- Scroll to the bottom to CHECK “I acknowledge that AWS CloudFormation might create IAM resources.”
- Click the orange “Create stack” button.
- Wait (a few minutes) for “CREATE_IN_PROGRESS” to change to “CREATE_COMPLETE”.
-
Click “Resources” in the horizontal menu.
If “ROLLBACK_IN_PROGRESS” appears, delete the stack and try again.
-
After “Initializing” turns to “checks passed” shows on all instances, dismiss the CloudShell and What is My IP Address tabs.
To SSH into the instance
Traditionally, to connect to a Windows instance GUI, a RDP client software program needs to be installed. Similarly, to connect to a Linux instance, a SSH client software program needs to be installed. Ditto with the VNC protocol.
However, Apache has done away with plugins or client software required by creating its Guacamole project to create a clientless remote desktop gateway.
VIDEO by Dean Bushmiller shows how to configure Guacamole HTML5 to access the Kali Linux instance. (10.0.0.5)
-
Duplicate another AWS browser tab and search for the “EC2” service for your region, instances, for a URL such as:
https://us-east-1.console.aws.amazon.com/ec2/home?region=us-east-1#Instances:instanceState=running
-
Click the Instance ID of the instance name ending with “bastion-guacamole”.
Client IP address
- Click the (copy to clipboard) icon to the left of the “Public IPv4 address” (such as 34.205.166.115).
- Open another browser tab and paste the IP address into the address bar to see the Guacamole login page.
- Click “Advanced” to “Your connection is not private”.
- Click the link such as “Proceed to 34.205.166.115 (unsafe)” for the “APACHE GUACAMOLE” login page.
- Click “Allow”.
-
Type “guacadmin” for the Username.
Get password within logs
- Click “Actions” drop-down to select “Monitor and troubleshoot”, and “Get system log”.
- Click in the log and press Ctrl-F to search for “password”.
-
Highlight and copy the password text such as “WKO0Kq7kJw9N” in:
Setting Bitnami application password to 'WKO0Kq7kJw9N'
- Paste the password. Click “Login”.
-
At the upper-right, click “guacadmin”, then “Settings”, “New Connection” to fill in fields:
-
Copy and paste to connect to Kali Linux
- Name: kali
- Protocol: RDP
- Maximum number of connections: 1
- Maximum number of connections per user: 1
Skip down to: PARAMETERS | Network
- Hostname: 10.0.0.4
- Port: 3390 Authentication:
- Username: kali
- Password: kali
Leave the rest blank.
- Scroll down to click “Save”.
-
At the upper-right, click “guacadmin”, then “Home”, then that “Kali”.
Victim Ubuntu config
This is optional unless you want to confirm a Man-in-the-Middle impact.
Ansible scripts may be used to configure.
- At the upper-right, click “guacadmin”, then “Settings”, “New Connection” to fill in fields:
-
Copy and paste
- Name: VIC-NIX
- Protocol: SSH
- Maximum number of connections: 1
- Maximum number of connections per user: 1
Skip down to: PARAMETERS | Network
- Hostname: 10.0.0.10
- Port: 22 Authentication:
- Username: vagrant
- Password: vagrant
-
Scroll down to click “Save”.
Victim Windows 2008 R2 config
This is optional unless you want to confirm a Man-in-th-Middle impact.
Ansible or PowerShell scripts may be used to configure.
- At the upper-right, click “guacadmin”, then “Settings”, “New Connection” to fill in fields:
-
Copy and paste
- Name: VIC-WIN
- Protocol: RDP
- Maximum number of connections: 1
- Maximum number of connections per user: 1
Skip down to: PARAMETERS | Network
- Hostname: 10.0.0.21
- Port: 3389 Authentication:
- Username: vagrant
- Password: vagrant
- Security mode: RDP encryption
-
Scroll down to click “Save”.
-
Now, hack away! see Kali PenTesting.
https://github.com/deanbushmiller/CEH-bootcamp/tree/master/4Day/LAB-Capture-pcapng
Stop instances
-
In AWS EC2, click the Instance ID of the instance name ending with “bastion-guacamole”.
CloudFormation phase:
-
Go to AWS CloudFormation console
https://console.aws.amazon.com/cloudformation/home
-
Select the stack you built previously and click Delete.
This deletes all resources for the solution (except the three copied AMIs; see below)
Delete the copied AMIs:
- Go to the EC2 Console > AMIs.
- Find the three AMIs that were created earlier with the copy commands and deregister them
-
After deregistering the AMIs, go to Snapshots in the EC2 Console
There will be three snapshots associated with the deleted AMIs that you can delete.
Juice Shop
Perhaps the most modern sample vulnerabler web app is Juice Shop maintained by OWSAP by volunteers at https://juice-shop.herokuapp.com/ book: “Pwning OWASP Juice Shop” at https://bkimminich.gitbooks.io/pwning-owasp-juice-shop/content referencing code at https://github.com/bkimminich/juice-shop.
DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web Application (DVWA) at http://dvwa.co.uk with code at https://github.com/ethicalhack3r/DVWA is a PHP/MySQL web application. So use XAMPP for its Apache web server and database.
BWA
Stand-up an instance of the BWA (Broken Web Application), a collection of intentionally vulnerable web applications distributed by OWASP in a Virtual Machine (VM) file used by Virtualbox, HyperV. VMware Workstation on Windows or VMware Fusion on Mac:
-
Instantiate a server. In Sep 2017 nested VT-x is supported on GCE, according to Paul R. Nash, Group Product Manager, Google Compute Engine.
- Open a Terminal console on the server and create/navigate to a folder for the project.
- Download the download file:
curl -O https://sourceforge.net/projects/owaspbwa/files/latest/download
% Total % Received % Xferd Average Speed Time Time Time Current Dload Upload Total Spent Left Speed 100 641 100 641 0 0 1781 0 --:--:-- --:--:-- --:--:-- 1785 - Confirm:
ls -al download
The OWASP_Broken_Web_Apps_VM_1.2.7z file downloaded is 1.7 GB (big!) because it contains various apps in Ruby, PHP, WordPress, etc.
It’s briefly described at https://owaspbwa.org, which resolves to https://code.google.com/archive/p/owaspbwa/
Note it’s from 2015.
- Unpack the 7z file. Navigate into the folder.
-
Double-click on file OWASP Broken Web Apps.vmx to open image in Virtualbox or VMWare workstation:
See Install video (music only, no dialog) [5:49]
-
Use it.
Video showing version 1.1.1 [21:53] by Chuck Willis shows how to use BWA to demonstrate occurance of “Top 10” vulnerabilities described by OWASP. Mutillidae:

http://www.concise-courses.com/infosec/owasp-broken-web-applications/
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FOEFL8bbbCU [7:05]
Beyond 1.0 from 2013 Chuck Willis (@chuckatsf) describes BWA origins
VAmPI (Python Flask)
https://github.com/erev0s/VAmPI (described in erev0s.com) is written in Python Flask as a target app that fails evaluation by tools that detect security issues described in OWASP Top 10 vulnerabilities for APIs.
No one wants switches to add vulnerabilities in productive code. But code & app generators such as Outsystems and Mendix can.
Nevertheless, VAmPI can be used for learning/teaching:
- Install Docker, Docker Compose, Postman, escape.tech, etc.
-
Generate OpenAPI (Swagger) specs for use by escape.tech to evaluate the running app’s security, such as this json. Outsystems generates that documentation automatically.
-
Generate a Collection file for explorating within Postman
-
At https://app.escape.tech/, specify the app’s endpoint URL.
- upload Escape’s https://gontoz.escape.tech/graphql
-
https://vampi.tools.escape.tech/
- Start: docker run -p 5000:5000 erev0s/vampi:latest
- Fork, then git clone https://github.com/???/VAmPI
- git remote add upstream https://github.com/erev0s/VAmPI
-
In another Terminal tab at VAmPI root containing docker-compose.yaml: docker-compose up -d
✔ Container vampi-secure Started 0.1s ✔ Container vampi-vulnerable Started
-
Run user emulator to:
- Create database
- Issue GET unauthenticated requests
-
Create account
- Login using Token-Based Authentication (Adjust lifetime from within app.py)
- Add books
- Retrieve books without secrets
-
Retrieve books with secrets
- Enable global configuration settings to switch specific vulnerabilities on or off during testing and confirmation.
DVIA iOS App Mobile Testing
The open-source “Damn Vulnerable iOS app” is written in Apple’s Swift language to provide an example to determine whether penetration testing tools and skills work in a legal environment.
It’s open-sourced at github.com/prateek147/DVIA-v2 for up to iOS 11.
Here we use docs defined by OWASP:
MASTG = Mobile Application Security Testing Guide
MASVS = Mobile Application Security Verification Standard
- Open Source Security Testing Methodology Manual (OSSTMM) is the basis for the Certified Hacker Analyst certification from the Institute for Security and Open Methodologies (ISECOM)
Setup:
- A paid Apple Developer account might be required.
-
Have a separate organizationally managed account using a business email setup at https://business.apple.com/signup
-
Using a organizationally managed accounts setup with a federated iDP (identity provider), an Apple Business Manager account (at https://business.apple.com) or Apple School Manager email is needed for role-based admin. such as reset passwords of Staff roles.
- On your iPhone Store, get the Apple Configurator
- https://support.apple.com/en-ae/guide/apple-configurator/apd97373af1e/ios
- Install the app.
-
Input fake data for you to find later.
- On a Apple Silicon MacBook, install the Apple Configurator App.
-
AppSync Unified
When using Windows or Linux, use AltStore, Cydia Impactor, etc.
AppSync Unified,
- Frida (Python)
- iRET
- iFunBox
- Ghidra
- Objection for injection (Python)
- KeyChain Dumper Passionfruit, GrapeFruit (dev version of PassionFruit)
- SQLite Browser
- Realm Browser from Apple Store
- https://github.com/ansjdnakjdnajkd/iOS
- Install Xcode.
- Fork github.com/prateek147/DVIA-v2 and clone to your account
- cd to the project root directory where the Podfile is present (/DVIA-v2/DVIA-v2).
- Run pod install
- Open the DVIA-v2.xcworkspace file with Xcode. 1. Run the app on a simulator.
- To run on the device, go under Project settings in Xcode on the top left, General tab and under Signing, enter credentials for your Apple ID.
- Guild and run the project on the device.
- Trust the app again under Settings -> General -> Device Management.
Certified DevSecOps Prateek Gianchandani of Dubai (highaltitudehacks.com)wrote DVIA to contain vulnerabilities which we aim to use various testing tools (such as MDM) to find, as described by Phil Keeble:
WARNING: On a test phone (not your personal phone):
- Local Data Storage
- Jailbreak Detection Bypass using CheckRa1n
- Excessive Permissions
- Runtime Manipulation
- Anti Anti Hooking/Debugging
- Binary Protection
- Touch/Face ID Biometric Bypass
- Phishing
- Side Channel Data Leakage
- IPC Issues
- Broken Cryptography
- Webview Issues
- Network Layer Security
- Application Patching
- Sensitive Information in Memory
Software Testing Guidelines
Guidance for planning and reporting of testing:
PTES
PTES (Penetration Testing Execution Standard) in 2009 defined phases of a pen-test engagement:
- Intelligence Gathering
- Pre-engagement Interactions
- Threat Modeling
- Vulnerability Analysis
- Exploitation
- Post Exploitation
- Reporting
The PTES Technical Guidelines is an “oldie but goodie” from 2014, but still has good wisdom.
OSSTMM STAR
PDF: form: STAR (Security Test Audit Report) is a standardized form to summarize results of a security or penetration test - providing precise calculations of the Attack Surface, details of what was tested and how, and indemnification for testing organization.
OSSTMM (Open Source Security Testing Methodology Manual) v3 PDF updated every six months by the ISECOM (Institute for Security and Open Methodologies). It was developed in an open community, and subjected to peer and cross-disciplinary review. ISECOM’s PDF: Security Test Audit Report (STAR) is a standardized form to summarize results of a security or penetration test - providing precise calculations of the Attack Surface, details of what was tested and how, and indemnification for testing organization.:
- Posture review
- Logistics
- Active Detection Verification
- Visibility Audit
- Access Verification
- Trust Verification
- Controls Verification
- Process Verification
- Configuration and Training Verification
- Property Validation
- Segregation Review
- Exposure Verification
- Competitive Intelligence Scouting
- Quarantine Verification
- Privileges Audit
- Survivability Validation and Service Continuity
- End Survey, Alert, and Log Review
OSSTMM has five channels or operational areas:
- Human Security: The security of human interaction and communication is evaluated operationally as a means of testing
- Physical Security: The OSSTMM tests physical security, defined as any tangible element of security that takes physical effort to operate
- Wireless Communications: Electronic communications, signals, and emanations are all considered wireless communications that are part of the operational security testing
- Telecommunications: Whether the telecommunication network is digital or analog, any communication conducted over telephone or network lines is tested in the OSSTMM
- Data Networks: The security testing of data networks includes electronic systems and data networks that are used for communication or interaction via cable and wired network lines
Security Testing Tools
DevSecOps is a practice of integrating security into the DevOps process.
Ethical Hacking tools
Many tools are used by Penetration Testers to attack systems and applications for the sake of finding vulnerabilities.
-
Kali Linux server
-
Metasploit
-
wazuh.com - https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=O5QnGeaLGIs Ubuntu
IAST (Interactive App Security Testing)
IAST (Interactive App Security Testing) was invented by Checkmarx, which adds an agent running along the app to report to a central “Security Handler”.
DAST (Dynamic Application Security Testing)
DAST aims to expose security weaknesses by watching application behavior while user actions are performed by automated scripts in a test environment, where various combinations of input actions are tried.
The main targets of a DAST system involve what offers a front door to attackers: HTTP and HTML – protocols that drive the World Wide Web.
Among DAST tools: web app penetration testing tools:
A. The Zed Attack Proxy (ZAP) is offered free, and is actively maintained by hundreds of international volunteers. Use it to scan for security vulnerabilities in your web applications while you are developing and testing your applications.
B. WebInspect from MicroFocus (formerly HP).
C. Burp Suite from Portswagger ($399/year Pro) with extensions, running on Kali Linux with FoxyProxy on Firefox, JPython, JRuby
D. Dirtbuster
E. VIDEO: ForAllSecure
SAST
SAST (Static App Security Testing) tools focus on scanning application source code for vulnerabilities in coding. Static Application Security Testing (SAST) vendors include:
- Veracode
- Perforce
- http://www.castsoftware.com/
- Checkmarx, which adds an agent running along the app to report to a central Security Handler, called Interactive App Security Testing (IAST).
Security tests should also cover the efficacy of Runtime Application Self-Protection (RASP) built within apps, rather than relying completely on the infrastructure Web Application Firewall (WAF).
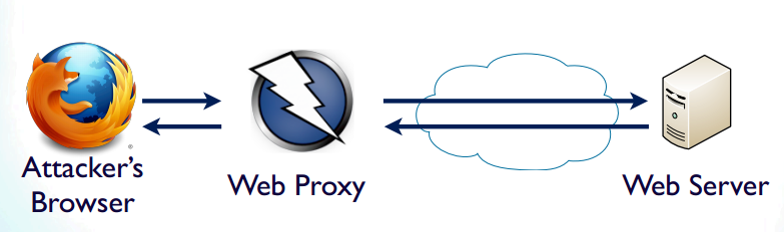
Install proxy server
There are several ways to obtain and instantiate a proxy server.
SaaS
QUESTION: Who are SaaS vendors operating on public cloud?
From Docker Hub
For those working on public clouds:
- Bring up Docker
- In a Terminal,
-
Use the Docker image provided by the OWASP organization at https://hub.docker.com/r/owasp/zap2docker-stable/
docker pull owasp/zap2docker-stable
docker images say it’s 1.33GB.
Alternately, for use in CI environments:
docker pull owasp/zap2docker-bare
docker images say it’s 525 MB, which is a third of the stable edition.
The images above were created based on code at: https://github.com/zaproxy/zaproxy/tree/develop/build/docker
ZAP’s project leader is Simon Bennetts (@psilnon). His lecture on 2 Jun 2015 [59:59]: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_MmDWenz-6U
-
Start ZAP in with xvfb (X virtual frame buffer) which allows add-ons that use Selenium (like the Ajax Spider and DOM XSS scanner) to run in a headless environment. Firefox is also installed so can be used with these add-ons.
Alternately: Start ZAP in headless mode with following command:
docker run -u zap -p 8080:8080 -i owasp/zap2docker-bare zap.sh -daemon -host 127.0.0.1 -port 8080
Blogs about this:
- https://github.com/zaproxy/zaproxy/wiki/Docker
On private servers
-
Download
wget -q -O - https://github.com/zaproxy/zaproxy/releases/download/2.4.3/ZAP_2.4.3_Linux.tar.gz
CAUTION: Enterprise security should review this.
-
Un-tar
tar zxf - -C /opt ln -s /opt/ZAP_2.4.3 /opt/zap
-
Since ZAP does not come with a script, this script for Debian:
wget -q -O /etc/init.d/zap https://raw.githubusercontent.com/stelligent/zap/master/packer/roles/zap/files/zap-init.sh chmod 755 /etc/init.d/zap
Instantiate within Google Cloud
Browser Proxy Setup
In Chrome:
- Menu > settings
- Proxy
In Firefox:
- Manu > Options
- Advanced
- Network tab
- Connections > Settings
- Clear “No Proxy for:” box
In Internet Explorer:
- Tools
- Internet options
- Connections tab
- Lan settings
-
Check proxy settings
-
Use http://localhost or
http://127.0.0.1:8080to reach the Proxy. - Automate settings:
In Firefox:
- Menu > Add-ons (shift+command+A)
- Click “See more Add-ins”
- In “Search for add-ons” search box, type “foxy boxy basix”.
- Select “FoxyProxy Standard”.
- Click “+ Add to Firefox”.
- Click “Add” in the pop-up.
- Restart now.
Install Jenkins plugin
Blogs:
- https://stelligent.com/2016/04/28/automating-penetration-testing-in-a-cicd-pipeline/
- https://stelligent.com/2016/05/11/automating-penetration-testing-in-a-cicd-pipeline-part-2/
The plug-in is at:
https://wiki.jenkins.io/display/JENKINS/zap+plugin
-
ZAP is written in Java, so a Java SDK is needed to run it.
https://github.com/zapproxy/zapproxy/wiki/
ZAP UI OWASP
The drop-down at the upper-left corner of the ZAP UI provides for 4 modes:
- Safe mode
- Standard mode
- Protected mode
-
Attack mode for sites you have permission to penetrate.
-
Click Quick Start to, on the Information window, input the URL to scan, starting with
https.The left pane Tree window provides the context history of URLs visited.
-
Run ZAP using the ‘standard’ zap.sh script.
There is also a zap-x.sh script which first starts xvfb (X virtual frame buffer) - this allows add-ons that use Selenium (like the Ajax Spider and DOM XSS scanner) to run in a headless environment.
ZAP scripts
The plugin:
- Manage Sessions (Load or Persist)
- Define Context (Name, Include URLs and Exclude URLs)
- Attack Contexts (Spider Scan, AJAX Spider, Active Scan)
You can also:
- Setup Authentication (Form Based or Script Based)
- Run as Pre-Build as part of a Selenium Build
- Generate Reports (.xhtml, .xml, .json)
Vendors
Sonatype
by TheDevOpsSchool Fundamental Tutorial for Beginners by Rajesh Kumar
SonarQube
Other DAST vendors
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_tools_for_static_code_analysis
-
Veracode Vulnerability Scanning Tools which only scans Java, were acquired on Nov 5 2018 from Broadcom by private equity firm Thoma Bravo who also funded Compuware and Dynatrace, Solar Winds and McAfee *
-
WebInspect from OpenText (formerly MicroFocus, formerly HP, formerly Mercury), a part of the Fortify suite, which consists of Fortify the SAST product.
-
Checkmarx.com, based in Israel, offers Codebashing, a developer education platform for secure coding training.
-
Synopsys.com [Wikipedia] acquired CodeDX, Black Duck, Coverity, and Cigital SecureAssist (a lightweight IDE plugin that points out common security vulnerabilities in real time).
-
IBM AppScan
-
Tenable.io by Nessus
SARIF
Static code analysis tool vendors have begun using the SARIF (Static Analysis Results Interchange Format) to publish results of their assessment of programming and style errors, non-compliance with legal requirements, and security vulnerabilities. The JSON-based format standard was published by industry group OASIS to provide a common output format to make it feasible for developers and teams to view, understand, interact with, and manage the results produced by several vendors.
-
The first version of the format was published in March 2020 as SARIF v2.1.0 to recognize Microsoft’s previous efforts and pre-standard versions. Its 220 pages in htm web page. Source code in pdf, docx, htm for the document is at:
- https://docs.oasis-open.org/sarif/sarif/v2.1.0/sarif-v2.1.0.html
- https://www.oasis-open.org/committees/tc_home.php?wg_abbrev=sarif
-
Tutorial:
-
In Visual Studio Code, install the “Microsoft SARIF Viewer” from Microsoft Dev Labs.
-
Clone the sample SARIF file from
https://github.com/microsoft/sarif-tutorials
-
Load a sample SARIF file into the viewer within Microsoft Visual Studio Code. Examine details:
- The location of the flaw and code paths leading to it
- The rule violated
- The severity of the violation (severe to minor, “error,” “warning”, “note”)
- Suggestions for remedying the problem
- When it’s ok to ignore the result
-
Load sample SARIF files into Microsoft.
Cartey and Keaton, OASIS SARIF TC co-chairs, said that “The next major version of SARIF will expand our ability to aggregate data and detect vulnerabilities in some exciting new ways.”
-
Clone a folder containing workflow and sample known-bad Terraform file.
-
Generate SARIF Using the tfsec GitHub Action from almost blank repo:
name: Run tfsec sarif report on: push: branches: [main, 'release/*'] pull_request: jobs: tfsec: name: tfsec sarif report runs-on: ubuntu-latest steps: - name: Clone repo uses: actions/checkout@main - name: Run sarif report uses: aquasecurity/tfsec-sarif-action@v0.1.0 with: sarif_file: tfsec.sarif - name: Upload SARIF file uses: github/codeql-action/upload-sarif@v1 with: # Path to SARIF file relative to the root of the repository: sarif_file: tfsec.sarifgit checout -b add-workflow
Resources
VIDEO: Overview of the 2021 OWASP Top 10 by John Wagnon while he was at F5.
STAR: Daniel Miessler’s https://danielmiessler.com/projects/webappsec_testing_resources
Getting Started with OWASP Zed Attack Proxy (ZAP) for Web Application Penetration Testing 1h 40m video course 16 Feb 2017 by Mike Woolard
STAR: https://python-security.readthedocs.io/security.html
https://www.securecoding.com/blog/python-security-practices-you-should-maintain/
More on Security
This is one of a series on Security in DevSecOps:
- Security actions for teamwork and SLSA
- Code Signing on macOS
- Git Signing
- GitHub Data Security
- Azure Security-focus Cloud Onramp
- AWS Onboarding
- AWS Security (certification exam)
- AWS IAM (Identity and Access Management)
- SIEM (Security Information and Event Management)
- Intrusion Detection Systems (Goolge/Palo Alto)
- SOC2
- FedRAMP
-
CAIQ (Consensus Assessment Initiative Questionnaire) by cloud vendors
- AKeyless cloud vault
- Hashicorp Vault
- Hashicorp Terraform
- SonarQube
- WebGoat known insecure PHP app and vulnerability scanners
- Security certifications
- Quantum Supremecy can break encryption in minutes
- Pen Testing
- Threat Modeling
- WebGoat (deliberately insecure Java app)
More on DevOps
This is one of a series on DevOps:
- DevOps_2.0
- ci-cd (Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery)
- User Stories for DevOps
- Git and GitHub vs File Archival
- Git Commands and Statuses
- Git Commit, Tag, Push
- Git Utilities
- Data Security GitHub
- GitHub API
- Choices for DevOps Technologies
- Pulumi Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
- Java DevOps Workflow
- AWS DevOps (CodeCommit, CodePipeline, CodeDeploy)
- AWS server deployment options
- Cloud services comparisons (across vendors)
- Cloud regions (across vendors)
- Azure Cloud Onramp (Subscriptions, Portal GUI, CLI)
- Azure Certifications
- Azure Cloud Powershell
- Bash Windows using Microsoft’s WSL (Windows Subsystem for Linux)
- Azure Networking
- Azure Storage
- Azure Compute
- Digital Ocean
- Packer automation to build Vagrant images
- Terraform multi-cloud provisioning automation
-
Hashicorp Vault and Consul to generate and hold secrets
- Powershell Ecosystem
- Powershell on MacOS
- Jenkins Server Setup
- Jenkins Plug-ins
- Jenkins Freestyle jobs
- Docker (Glossary, Ecosystem, Certification)
- Make Makefile for Docker
- Docker Setup and run Bash shell script
- Bash coding
- Docker Setup
- Dockerize apps
- Ansible
- Kubernetes Operators
- Threat Modeling
- API Management Microsoft
- Scenarios for load
- Chaos Engineering
2025-07-24 00:00:00 +0000



